
The React Native New Architecture, Trends, and Features
Quick Summary
What is the React Native New Architecture in 2025, and why should you care?
2025 is a decisive year for teams building with React Native. The framework’s New Architecture, centered on React Native Fabric and TurboModules, plus JSI, has officially moved from experimental to production-ready. According to the React Native blog, more than 90% of core modules now support the new system, making upgrades both feasible and urgent. Alongside this, the Hermes engine is now the default runtime, delivering up to 30% faster startup times, smaller bundle sizes, and better memory efficiency.
This blog breaks down why 2025 is the turning point for React Native adoption. We explored the stability of versions 0.75–0.80, the performance advantages of Hermes, practical migration steps, and enterprise-scale best practices like CI/CD and monorepo strategies. We also shared a performance checklist for 2025 and looked ahead at future roadmap themes, including deeper engine improvements and better tooling. The bottom line: upgrading today means compounding wins tomorrow; faster apps, happier users, and a future-proof mobile stack.
Introduction
2025 is the decisive year for React Native. The framework’s new architecture, which is built on Fabric, TurboModules, and JSI, has finally moved from testing to being ready for real-world apps. As the React Native blog notes, over 90% of core modules now support it, which means upgrading is not only possible but strongly recommended. At the same time, the Hermes engine is now the default, giving apps up to 30% faster startup times, smaller downloads, and better memory use.
For your business, this translates into faster apps, smoother animations, and lower maintenance costs with each new release.
In this guide, we will cover what is new in 2025: the state of the new architecture, Hermes performance boosts, important version updates, and a step-by-step migration plan. If you want expert help, our mobile app development experts can guide you through upgrades without downtime.
The React Native New Architecture: Fabric, TurboModules, and JSI — Where Things Stand
The React Native New Architecture (NA) in React Native is a complete rebuild of how the framework connects JavaScript with native code. It has three main parts:
- Fabric: The new rendering system for UI.
- TurboModules: a faster, lightweight way to connect JavaScript with native modules.
- JSI (JavaScript Interface): a modern bridge that allows direct calls between JS and native code without extra overhead.
Together, these improvements replace the old “bridge” system, making apps feel faster, smoother, and closer to native performance. For businesses, this means:
- Smoother UI and animations — better user experience.
- Reduced performance overhead — faster app responses.
- Easier scaling — teams can build more complex apps with less friction.
For a deeper dive into the New Architecture, you can see the official React Native documentation.
Planning for a major refactor? It is smart to work with an enterprise-grade software development partner to ensure migrations are handled without breaking production.
Fabric: The Modern Renderer for Smoother UI
React Native Fabric and TurboModules are at the heart of the New Architecture. Fabric specifically modernizes the rendering layer, ensuring smoother UI updates, improved list handling, and more consistent layouts across iOS and Android. For businesses, this translates to better animation stability, reduced UI glitches, and a more native-like performance baseline. Fabric is React Native’s new rendering system. Instead of relying on legacy rendering, Fabric brings:
- Better handling of complex lists (like FlatList, FlashList).
- Consistent layouts across iOS and Android.
- Improved animations and transitions.
This is especially useful for apps that rely on infinite scrolling, dashboards, or real-time feeds, where performance and smoothness are most crucial.
TurboModules: Faster Native Bridges, Less Overhead
Alongside Fabric, React Native Fabric and TurboModules work together to reduce the legacy bridge’s overhead. TurboModules only load when required, saving memory and improving runtime efficiency. By batching work more effectively, TurboModules improve app responsiveness and help apps scale cleanly across complex feature sets.
TurboModules are a faster, more efficient way of connecting JavaScript code to native modules. Compared to the legacy module system, TurboModules offer:
- Lazy Loading: modules load only when needed, reducing startup time.
- Batching Support: multiple calls can be processed together, lowering overhead.
- Better Memory Efficiency: no pre-loading of unused modules.
This means smaller apps, quicker launches, and lower device strain, all of which directly improve user retention.
JSI: Direct Bindings for Speed and Flexibility
The JavaScript Interface (JSI) is the backbone of the New Architecture. Unlike the old bridge, JSI:
- Allows direct, synchronous calls between JavaScript and native code.
- Removes the JSON serialization bottleneck.
- Opens the door to new integrations like custom rendering engines, third-party native libraries, and more advanced memory management.
In short, JSI gives React Native the flexibility to evolve like a native-first framework while keeping the developer-friendly JavaScript layer intact.
Old Bridge vs New Architecture in React Native


React Native New Architecture (Fabric, TurboModules, JSI): The new architecture replaces the old bridge with a faster, modular system for smoother UI, reduced overhead, and more native-like performance.
Key Differences:
- Bridge removed → direct JS ↔ Native communication.
- Faster startup → no pre-loading unused modules.
- Smoother UI → Fabric ensures consistent rendering across platforms.
- Future-ready → easier to integrate new engines, libraries, and tools.
Hermes Engine in React Native 2025: Faster Starts, Smaller Apps
One of the biggest milestones for React Native in 2025 is that Hermes is now the default JavaScript engine across all new projects. Earlier, developers could choose between Hermes and JavaScriptCore (JSC), but with Hermes officially replacing JSC in modern versions, the ecosystem is fully aligned toward performance-first mobile apps.
What does this mean for your business? Apps built with Hermes benefit from:
- Faster Startup Times: Benchmarks show upto 30% improvement in cold start performance, which directly improves user retention.
- Reduced Memory Usage: Hermes is optimized for low-resource environments, ensuring smooth operation on both entry-level and flagship devices.
- Smaller Bundle Sizes: Hermes compiles JavaScript to bytecode ahead of time, reducing overall app size and improving install rates.
- Consistency Across Platforms: With JSC support dropped, teams no longer juggle different engines or compatibility issues.
By standardizing Hermes, React Native ensures that every new release compounds into faster apps and more efficient resource usage, critical advantages for apps that need to scale globally.
Contextual Insight: measuring startup time improvements or memory usage often requires in-depth profiling. If you are planning to upgrade and want clear visibility into your performance gains, partner with our mobile app development team for expert support.
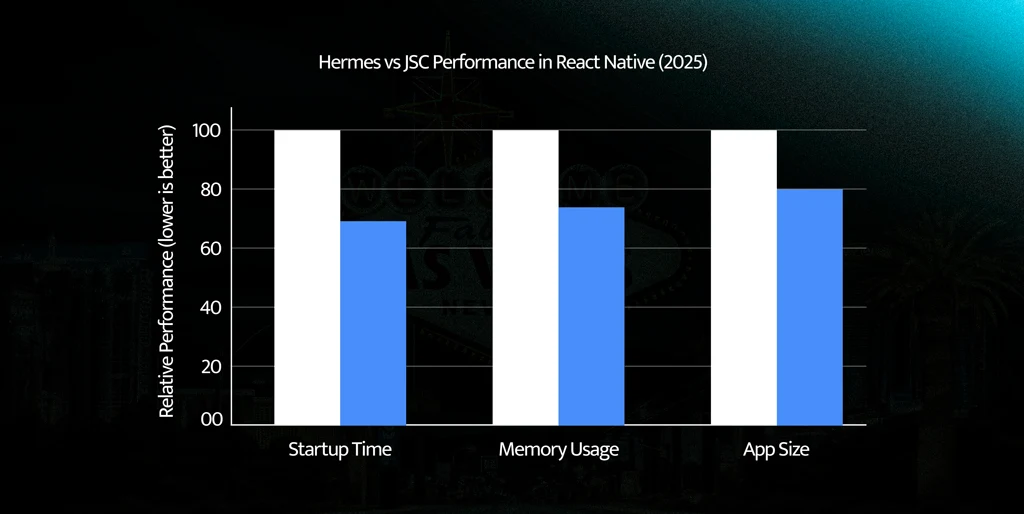
Hermes vs JSC Performance (2025): Hermes consistently outperforms JavaScriptCore, offering faster startup times, lower memory usage, and smaller app sizes, making it the clear choice for modern React Native apps.
React Native 0.75–0.80 Features: Stability, Speed, and Why It Matters
The React Native team has been steadily pushing the framework toward long-term stability and scalability. Between version 0.75 and version 0.80, several key milestones shaped how teams should plan their upgrades:
1. Fabric & TurboModules Reach Maturity
These core pillars of the New Architecture are now stable and widely adopted. Fabric ensures consistent rendering across platforms, especially for complex lists and animations, while TurboModules reduce overhead by optimizing the way JavaScript talks to native code. Together, they bring apps closer to true native-like performance.
2. Hermes as the Standard Runtime
By version 0.76+, Hermes became the default engine, and JSC support was phased out. Hermes now includes improved garbage collection, reduced memory leaks, and smaller app bundle sizes, making apps faster on startup and lighter to install, critical for markets where device storage and network bandwidth are limited.
3. Developer Experience Upgrades
Codegen React Native for TurboModules is more reliable, debugging tools have improved, and the CLI experience has been streamlined. These enhancements lower the entry barrier for teams and reduce migration friction for existing apps.
4. Migration-Friendly Changes
With each incremental release, the React Native team has prioritized backward compatibility where possible and published clearer migration guides. This means that upgrading incrementally (e.g., 0.77 -> 0.78) is significantly less painful than large version jumps used to be.
Why This Matters for Your Business
Each release is not just about new features; it is about compounding efficiency:
- Fewer bugs and regressions due to upstream fixes.
- Better user experience through smoother UI and faster app startup.
- Reduced engineering time spent on patching or workarounds.
- Longer shelf-life for apps by aligning with the community’s roadmap.
The smartest strategy is to target the latest stable React Native version and implement a continuous upgrade cycle. This ensures your app stays secure, performant, and cost-efficient.
Need expert support? WEDOWEBAPPS’s react native specialists can help you create a low-risk upgrade plan personalized to your app.

React Native Migration Guide: Upgrading to the New Architecture Without Downtime
For businesses with mature React Native apps, adopting the New Architecture is not just a technical upgrade; it’s a strategic investment in performance and scalability. The process can appear daunting, but by breaking it down into structured phases, you can migrate with confidence. Companies like Shopify have already walked this path and stress one key insight: focus on version upgrades first. Many migration blockers vanish once you’re on the latest stable React Native release.
Here’s a comprehensive react native upgrade guide designed for 2025:
1. Audit Your Dependencies (Know What You’re Working With)
- Review all third-party libraries in your project. Older dependencies built on the legacy Bridge may not support Fabric or TurboModules.
- Use tools like npm outdated or yarn outdated to spot lagging packages.
- For unsupported libraries, check if there are maintained forks or replacements. In some cases, you may need to wrap or rebuild modules using the new system.
Pitfall to avoid: Ignoring dependency compatibility can cause runtime crashes post-upgrade.
2. Upgrade React Native to the Latest Stable Release
- Move incrementally but aim for v0.80+ to unlock the most stable New Architecture support.
- Follow the official React Native Upgrade Helper for guided diffs.
- Ensure your CI/CD pipeline can handle the new toolchain (Gradle 8, Xcode 15, etc.).
Pro tip: Don’t skip too many versions in one go; debugging becomes exponentially harder.
3. Enable the New Architecture (Fabric + TurboModules)
- On Android, add newArchEnabled=true to your gradle.properties.
- On iOS, update the Podfile to opt into the new system.
- Run a clean build to ensure the new renderer and module system are activated.
This unlocks Fabric (new renderer) and TurboModules (faster native bridges).
4. Validate and Migrate Native Modules
- Check custom modules: If you’ve written native code, ensure it complies with TurboModules.
- Use Codegen to auto-generate type-safe bindings between JS and native code.
- Update or rewrite modules still tied to the legacy Bridge.
Pitfall to avoid: Mixing old and new modules can introduce subtle memory leaks.
5. Instrument Performance Monitoring
- Baseline your app before migration (startup time, memory usage, frame drops).
- After enabling the New Architecture, measure again. Tools like Flipper, React Profiler, and Systrace help visualize improvements.
- Track KPIs such as:
- TTI (Time to Interactive)
- Bundle size
- Average memory footprint
- Dropped frame percentage
Most apps report measurable wins once Hermes + Fabric are in place.
6. Rollout Gradually (Protect the User Experience)
- Start with internal or beta testers.
- Monitor logs, crash reports, and performance dashboards closely.
- Roll out in stages, especially if your app has millions of active users.
Pro tip: Use feature flags to enable Fabric/TurboModules selectively during rollout.
Shopify’s Guidance: Why Version First, Migration Later
Shopify’s engineers, who migrated a large-scale e‑commerce app, recommend focusing on keeping your React Native version current. Many bugs that seem like “migration blockers” are often fixed in upstream releases. By aligning with the latest stable, you reduce the burden of custom fixes and avoid maintaining brittle patches.
Business Takeaway
Migrating to the New Architecture is not just a developer task; it’s about ensuring your app remains performant, cost-efficient, and future-proof. A rushed migration can risk downtime, but a strategic, phased approach yields compounding benefits: faster apps, lower crash rates, and smoother scaling.
If your app powers critical business operations, consider partnering with an enterprise-grade software development partner to ensure a safe, end-to-end migration without interruptions.
React Native Performance Optimization: 2025 Practical Checklist & Performance Tips
Even with React Native’s New Architecture and Hermes engine making apps faster by default, performance tuning remains a competitive edge. In 2025, users expect instant load times, buttery-smooth animations, and battery-efficient apps. Here are some practical react native scaling best practices your team can apply to keep your React Native apps running at peak performance:
1. Bundle Size Optimization
- Code-splitting & lazy loading: Import heavy libraries only when needed.
- Tree-shaking: Remove unused code during build to shrink bundle size.
- Use dynamic imports: Split less frequently used features into separate chunks to reduce initial load.
Smaller bundles = faster startup and reduced memory footprint.
2. Image & Asset Strategy
- Use WebP or AVIF formats for compressed, high-quality assets.
- Leverage react-native-fast-image for caching and progressive loading.
- Resize images on the server before bundling them into the app.
Oversized assets are one of the biggest causes of app bloat.
3. Avoiding Unnecessary Re-renders
- Memoization with React.memo or useMemo to cache component results.
- useCallback hooks for stable function references.
- Selector libraries like Recoil or Zustand for efficient react native state management at scale.
Minimizing re-renders helps sustain smooth animations and maintain responsive interaction.
4. Virtualized & High-Performance Lists
- FlatList optimizations: use getItemLayout, removeClippedSubviews, and windowSize.
- FlashList by Shopify: a drop-in replacement with ~10x faster list virtualization.
- SectionList optimizations for large data sets.
Lists are a major performance bottleneck; optimizing them can reduce dropped frames drastically.
5. Monitoring & KPIs to Track
- Time to Interactive (TTI): how quickly the app feels usable.
- Dropped frames: especially during navigation or animations.
- Memory usage: detect leaks early with Flipper plugins.
- Startup time: compare Hermes vs legacy engines.
Continuous monitoring ensures optimizations don’t regress after updates.
6. React Native Animations Performance
One of the most visible wins of the React Native New Architecture is smoother animations. With Fabric as the modern renderer, UI updates and animations are now more consistent across iOS and Android. This reduces frame drops and makes interactions like scrolling lists or swiping gestures feel closer to native experiences.
For performance-heavy use cases—such as large lists, transitions, or complex UI gestures—developers should leverage the native driver to offload animation work from JavaScript to the native thread. Combined with tools like Reanimated 3 and FlashList, teams can push React Native animations performance to near-native levels, ensuring apps feel fluid even under high load.
7. React Native App Startup Time
A critical metric in React Native performance optimization is startup speed. Thanks to the Hermes engine, most apps already experience faster launches, but teams should also combine Hermes with lazy loading and code-splitting. This prevents unnecessary modules from blocking the first render, directly improving React Native app startup time. Monitoring KPIs like Time to Interactive (TTI) and memory usage ensures startup remains optimized as apps scale.
By prioritizing animation optimization in your React Native performance tips checklist, you not only improve user satisfaction but also reduce churn from laggy UI experiences.
Business Takeaway
Every millisecond saved adds up to a better user experience and happier customers. By investing in bundle optimization, smarter asset handling, and continuous monitoring, you not only improve app speed but also reduce long-term maintenance costs.
Need expert support to fine-tune your app’s performance? Our mobile app development experts can run dedicated optimization sprints to deliver measurable results.
Team & Architecture at Scale
Scaling React Native in 2025 is no longer just about writing efficient code; it’s about orchestrating teams, tooling, and processes so apps can grow without breaking down. At scale, enterprises face challenges of consistency, coordination, and release velocity, all of which demand deliberate architectural planning.
Monorepos and Codegen Consistency
Many large-scale React Native teams are adopting monorepo setups (using tools like Nx, Lerna, or Yarn workspaces). This enables shared libraries, consistent dependency management, and a unified codebase across multiple apps. Combined with Codegen, teams can enforce type safety between JavaScript and native layers, reducing integration bugs and future-proofing custom modules.
Design Systems & Shared UI
At enterprise scale, design-system integration becomes critical. Shared component libraries ensure brand consistency while reducing duplicated effort across feature teams. For example, centralizing typography, color tokens, and accessibility rules helps apps remain cohesive and compliant.
CI/CD and Release Pipelines
Shipping features rapidly and reliably means investing in automated pipelines:
- Continuous Integration (linting, tests, type checks).
- Continuous Deployment (automated builds, beta rollouts, crash monitoring).
- OTA (Over-The-Air) updates via CodePush or AppCenter for rapid iteration.
This helps large orgs maintain velocity without sacrificing stability.
Roles & Documentation to Prevent Regression
Scaling also changes team composition: you’ll likely need a mix of React Native developers, iOS/Android specialists, QA automation engineers, and DevOps staff. Equally important is a living documentation system; style guides, API contracts, and migration standards to ensure teams don’t reintroduce solved problems.
Why It Matters for Enterprises
A well-planned architecture at scale is not just a technical necessity; it’s a business enabler. Faster delivery, reduced regressions, and predictable releases allow enterprises to compete with agility. The React Native Working Group and GitHub repos are great sources for following evolving best practices.
Looking to scale your React Native delivery? Our Software Development team can help.
What’s Next on the Horizon?
As we look ahead, React Native’s trajectory is shaped by both the official roadmap and the community’s ongoing experimentation. While the New Architecture (NA) has moved from experimental to mainstream, 2025 will be about solidifying defaults and unlocking what’s next in performance and tooling.
Broader Adoption of the New Architecture
Fabric, TurboModules, and JSI React Native are expected to become fully standardized defaults across platforms. This means fewer conditional setups and more “out-of-the-box” consistency when starting new projects or migrating legacy ones. For developers, the benefit is less time spent on compatibility patches and more focus on building product features.
Better Tooling & Developer Experience
The ecosystem is also moving toward smoother upgrade paths and smarter tooling. Expect improvements in the React Native CLI, Flipper integrations, and Codegen react native automation to reduce friction during setup and migrations. These shifts aim to make day-to-day development as seamless as working with pure web frameworks, while keeping native power intact.
Deeper Engine Improvements
With Hermes now the default, conversations are shifting to engine-level enhancements, further reducing app startup times, optimizing memory use, and enabling new APIs that take advantage of direct JSI bindings. Some experimental work is already happening around multi-threading and graphics optimizations, which could push React Native apps even closer to native parity.
Why This Matters
While these directions are forward-looking and community-driven, they signal a steady evolution: React Native is positioning itself as a long-term, production-ready choice for startups and enterprises alike. Teams that keep pace with these react native trends 2025 will benefit from early stability, performance gains, and a future-proof stack.
React Native Roadmap 2025 and Upcoming Features
As React Native continues to mature, the 2025 roadmap points to a year of consolidation and react native upcoming features. The React Native community and core contributors are aligning around three major themes:
- Broader New Architecture adoption – With Fabric, TurboModules, and JSI React Native already production-ready, the next step is ensuring that more third-party libraries and tooling fully support this setup. By 2025, broader adoption means teams can migrate with fewer compatibility hurdles and enjoy performance gains out of the box.
- Better developer tooling – Expect continued improvements to debugging, profiling, and automation tools. From React Native performance tips built directly into Flipper to streamlined upgrade processes, the focus is on making developers more productive while reducing friction during app maintenance.
- Deeper Hermes improvements – The Hermes engine in React Native remains the default runtime, but upcoming updates promise further reductions in memory usage, faster garbage collection, and even better cold start performance.
In short, the React Native roadmap 2025 emphasizes stability, ecosystem readiness, and performance optimization; ensuring that teams adopting now can scale with confidence while preparing for future enhancements.
Conclusion: React Native in 2025, Built for Scale and Speed
The React Native of 2025 is not the same framework it was even a few years ago. With the New Architecture (Fabric, TurboModules, JSI) now production-ready and Hermes as the default engine, the framework delivers faster startup times, smoother UIs, and reduced maintenance overhead. Every upgrade compounds into long-term wins — better performance, easier scaling, and future-proof apps.
For teams, the message is clear: adopting the modern React Native stack isn’t optional, it’s strategic. Those who embrace continuous upgrades and performance optimization will deliver experiences that feel native while enjoying the productivity of JavaScript and React.
Looking at React Native for enterprise-scale delivery? Partner with our Software Development Company to align your product roadmap with the framework’s future.
Practical How-To Playbook for React Native Developers
- How to migrate an existing app to React Native’s New Architecture?
- Audit all project dependencies for compatibility with the latest React Native.
- Upgrade your project to the latest stable React Native version.
- Enable New Architecture settings individually on Android and iOS platforms.
- Test Fabric and TurboModules integration using official migration documentation guidance.
- Fix incompatible native modules and replace them with community-maintained alternatives.
- Validate app behavior, animations, and UI consistency across all devices.
- Use performance tools like Flipper to benchmark startup time improvements.
- Roll out the update gradually with staged releases to minimize risk.
- How to optimize React Native performance in 2025 apps?
- Reduce bundle size by lazy loading and splitting code effectively.
- Optimize images with responsive sizes, caching, and compression strategies.
- Avoid unnecessary re-renders using React.memo and useCallback effectively.
- Virtualize long lists with FlatList or FlashList for smoother scrolling.
- Enable Hermes engine to improve startup time and memory efficiency.
- Monitor dropped frames and TTI with Flipper or DevTools.
- Minimize heavy animations; prefer native driver for complex animation sequences.
- Regularly profile performance metrics and fix bottlenecks early during development.
- How to improve React Native app startup time effectively?
- Use Hermes engine, default in 2025, for faster app initialization.
- Reduce JavaScript bundle size with code splitting and lazy loading.
- Defer non-critical assets and load them after initial screen rendering.
- Use smaller, compressed images optimized for different device resolutions.
- Preload critical assets like fonts and icons during splash screen.
- Enable inline requires to load modules only when needed.
- Avoid heavy synchronous operations blocking the main JavaScript thread.
- Test cold start performance across devices using automated benchmarking tools.
- How to scale React Native teams and codebases in large enterprises?
- Adopt a monorepo setup with workspaces for shared code management.
- Use Codegen for consistency across Fabric and TurboModules implementations.
- Establish a design system to unify UI components across applications.
- Automate testing pipelines with CI/CD for reliable, fast releases.
- Assign cross-functional teams combining React Native and native developers.
- Write strong documentation to ensure consistency and reduce onboarding issues.
- Implement linting and type checking to prevent regressions in production.
- Track technical debt and schedule refactoring cycles to maintain quality.
- How to monitor React Native apps for performance and stability?
- Integrate Flipper plugins for real-time performance monitoring and debugging.
- Use React DevTools for profiling re-renders and checking state efficiency.
- Track app KPIs like TTI, memory usage, and frame drops.
- Implement logging with services like Sentry for runtime error reporting.
- Monitor network requests with tools to detect bottlenecks and failures.
- Use Firebase Crashlytics for crash reports and device-specific diagnostics.
- Automate regression testing before every release to catch hidden bugs.
- Collect user feedback continuously to spot performance pain points early.
Frequently Asked Questions
The New Architecture combines Fabric, TurboModules, and JSI to deliver smoother UIs, faster native integration, and reduced overhead.
Hermes is default because it provides faster startup times, smaller bundle sizes, and improved memory efficiency compared to JavaScriptCore.
While not forced, upgrading is strongly recommended to avoid deprecated modules, gain performance, and ensure long-term project stability.
Audit dependencies, review native module compatibility, and follow the official React Native upgrade guide.
Always target the latest stable release (currently 0.80+) to inherit security patches, bug fixes, and performance improvements.


